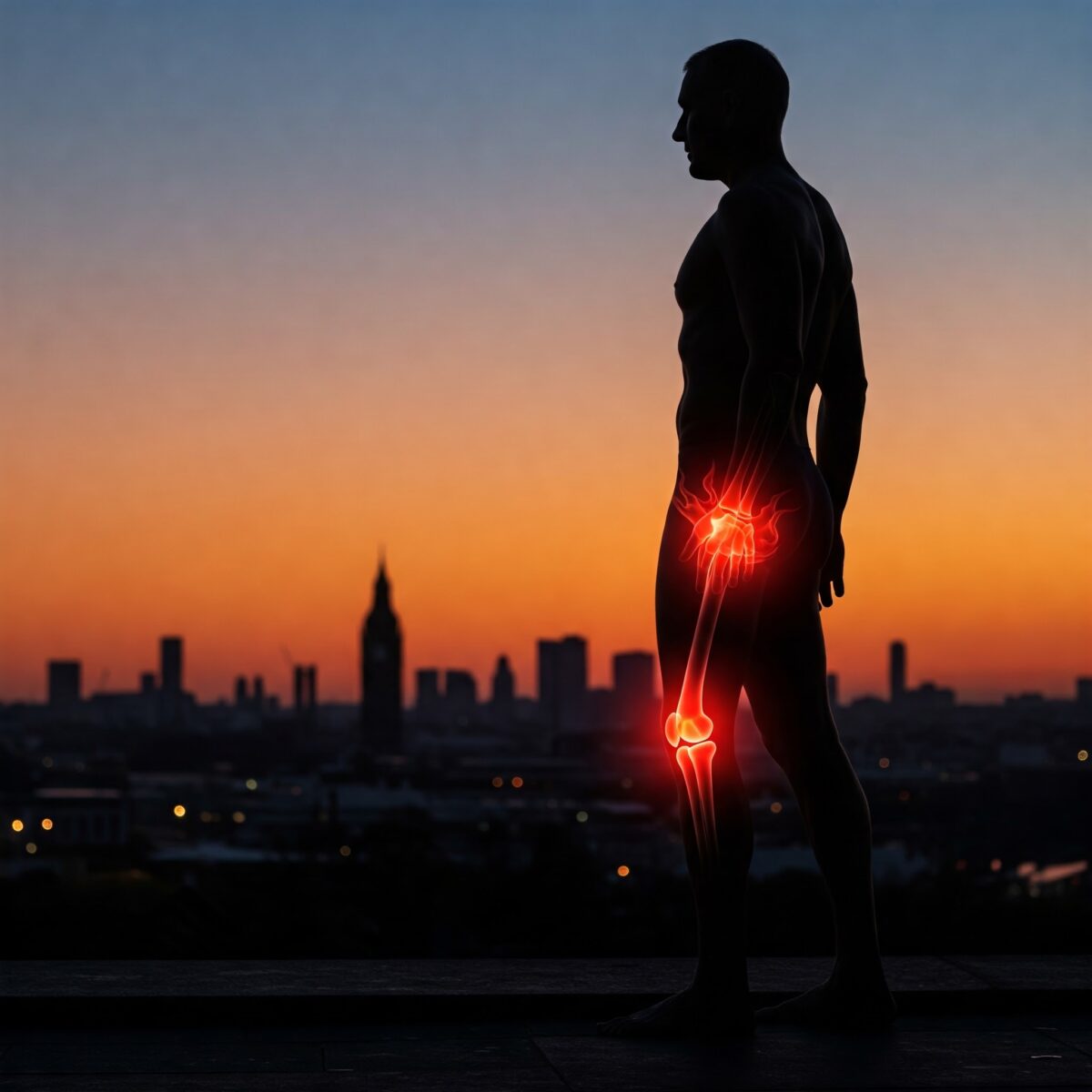
Mastering Inflammation for a Healthier You
Ever feel like your body is constantly fighting an invisible battle? You’re not alone. Inflammation, a natural defense mechanism, can sometimes turn rogue, becoming a silent driver behind a host of diseases, including cancer. This isn’t just about aches and pains; it’s a fundamental process impacting our physical and mental well-being right here in the UK.
Imagine a tiny spark meant to protect you, growing into a wildfire. That’s what chronic inflammation can do. It’s linked to heart disease, diabetes, Alzheimer’s, and yes, various cancers. But here’s the good news: you have more control than you think. We’re diving deep into the intricate relationship between inflammation and disease, exploring its impact on both body and mind, specifically within the UK context. Then, we’ll equip you with 12 powerful, actionable strategies to dial down inflammation and pave the way for a healthier, more vibrant life. Get ready to take charge of your health journey!
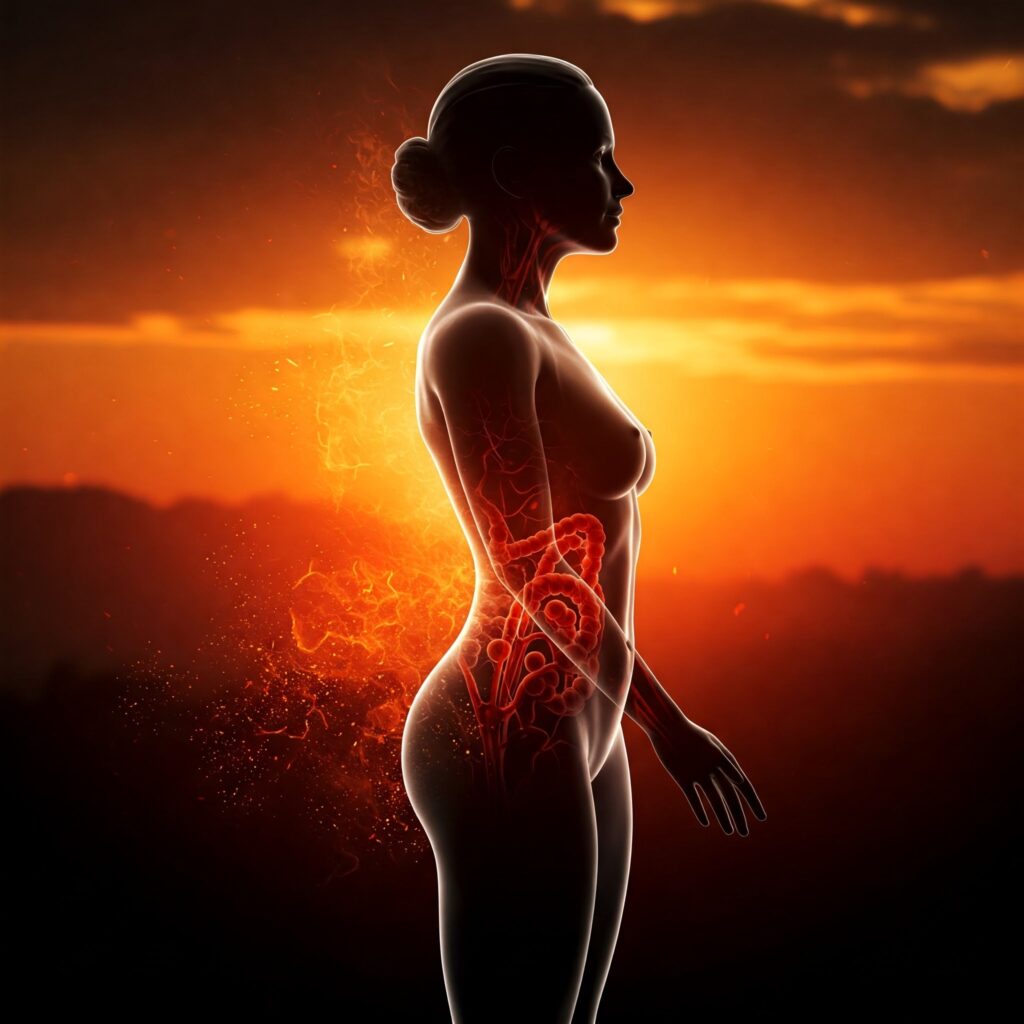

The Double-Edged Sword: Understanding Inflammation’s Role in Disease and Cancer (UK Focus)
Inflammation is a cornerstone of our immune system. When your body detects an injury or infection, it unleashes a cascade of biological responses designed to isolate and eliminate the threat, and initiate the healing process. Think of a sprained ankle: the redness, swelling, heat, and pain are all signs of acute inflammation doing its job. This short-term response is crucial for survival.
However, problems arise when this inflammatory response becomes chronic – a persistent, low-grade smoldering within the body. This is where the link to various diseases, including cancer, becomes significant. In the UK, the burden of chronic inflammatory diseases is substantial, impacting millions and contributing significantly to healthcare costs and reduced quality of life.
Inflammation and the Body: A UK Perspective
Consider cardiovascular disease, the leading cause of death in the UK. Chronic inflammation plays a pivotal role in the development of atherosclerosis, where fatty plaques build up in the arteries. Inflammatory cells contribute to this process, making the plaques unstable and increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Type 2 diabetes, another growing concern in the UK, is also closely linked to inflammation. Excess body fat can trigger a chronic inflammatory state, leading to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. This can eventually lead to high blood sugar levels and the development of diabetes.
Furthermore, many autoimmune diseases prevalent in the UK, such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis, are characterised by chronic inflammation. In these conditions, the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, leading to persistent inflammation and tissue damage. The impact on individuals’ lives can be significant, affecting mobility, energy levels, and overall well-being.
The Mind-Body Connection: Inflammation’s Impact on Mental Health
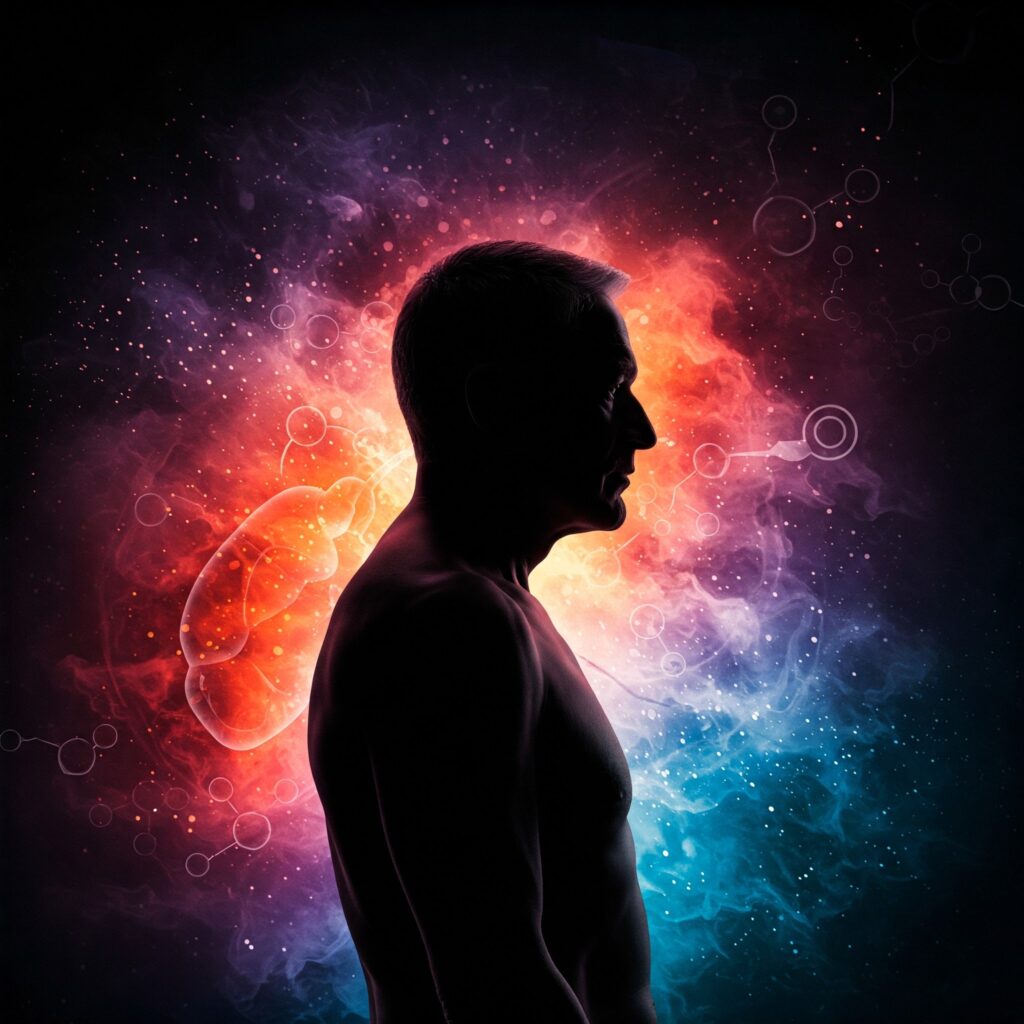

The reach of inflammation extends beyond the physical; it significantly impacts our mental well-being too. Research increasingly highlights the role of inflammation in various mental health conditions, a growing area of concern in the UK.
Depression, for instance, is no longer solely viewed as a chemical imbalance in the brain. Studies suggest that chronic inflammation can disrupt neurotransmitter function, affecting mood, energy levels, and cognitive function. Inflammatory markers have been found to be elevated in individuals with depression, and some evidence suggests that anti-inflammatory treatments may have antidepressant effects in certain cases.
Anxiety disorders, another prevalent mental health challenge in the UK, are also being investigated for their inflammatory components. While the exact mechanisms are still being unraveled, inflammation may contribute to the heightened state of arousal and fear associated with anxiety.
Emerging research also links inflammation to neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, a significant health concern for the aging population in the UK. Chronic inflammation in the brain is thought to contribute to the accumulation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles, the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s.
The Cancer Connection: How Inflammation Fuels Malignancy
The link between chronic inflammation and cancer is complex but increasingly well-established. In the UK, cancer remains a major health challenge, and understanding its underlying mechanisms is crucial for prevention and treatment.
Chronic inflammation can create a microenvironment that promotes the development and progression of cancer in several ways:
- DNA Damage: Inflammatory processes can generate reactive oxygen species (free radicals) that can damage DNA, increasing the risk of mutations that can lead to cancer.
- Cell Proliferation and Survival: Inflammatory signalling molecules can stimulate cell growth and inhibit programmed cell death (apoptosis), allowing pre-cancerous cells to survive and multiply.
- Angiogenesis: Tumours need a blood supply to grow and spread. Inflammatory factors can promote the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis) that nourish cancerous cells.
- Metastasis: Inflammation can facilitate the spread of cancer cells to other parts of the body (metastasis) by creating a favourable environment for their migration and invasion.
- Immune Evasion: Chronic inflammation can sometimes suppress the anti-tumour immune response, allowing cancer cells to evade detection and destruction by the immune system.
Several cancers have strong links to chronic inflammatory conditions. For example:
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Individuals with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis have an increased risk of colorectal cancer.
- Chronic Hepatitis: Long-term inflammation of the liver due to viral infections or other causes increases the risk of liver cancer.
- Chronic Pancreatitis: Persistent inflammation of the pancreas is a risk factor for pancreatic cancer.
- Asbestos Exposure: Inflammation caused by asbestos fibers can lead to mesothelioma, a type of cancer affecting the lining of the lungs.
It’s important to note that while chronic inflammation increases cancer risk, it doesn’t mean that everyone with a chronic inflammatory condition will develop cancer. The interplay of genetics, lifestyle factors, and the specific type and duration of inflammation all contribute to the overall risk.
Taking Control: 12 Ways to Reduce Inflammation
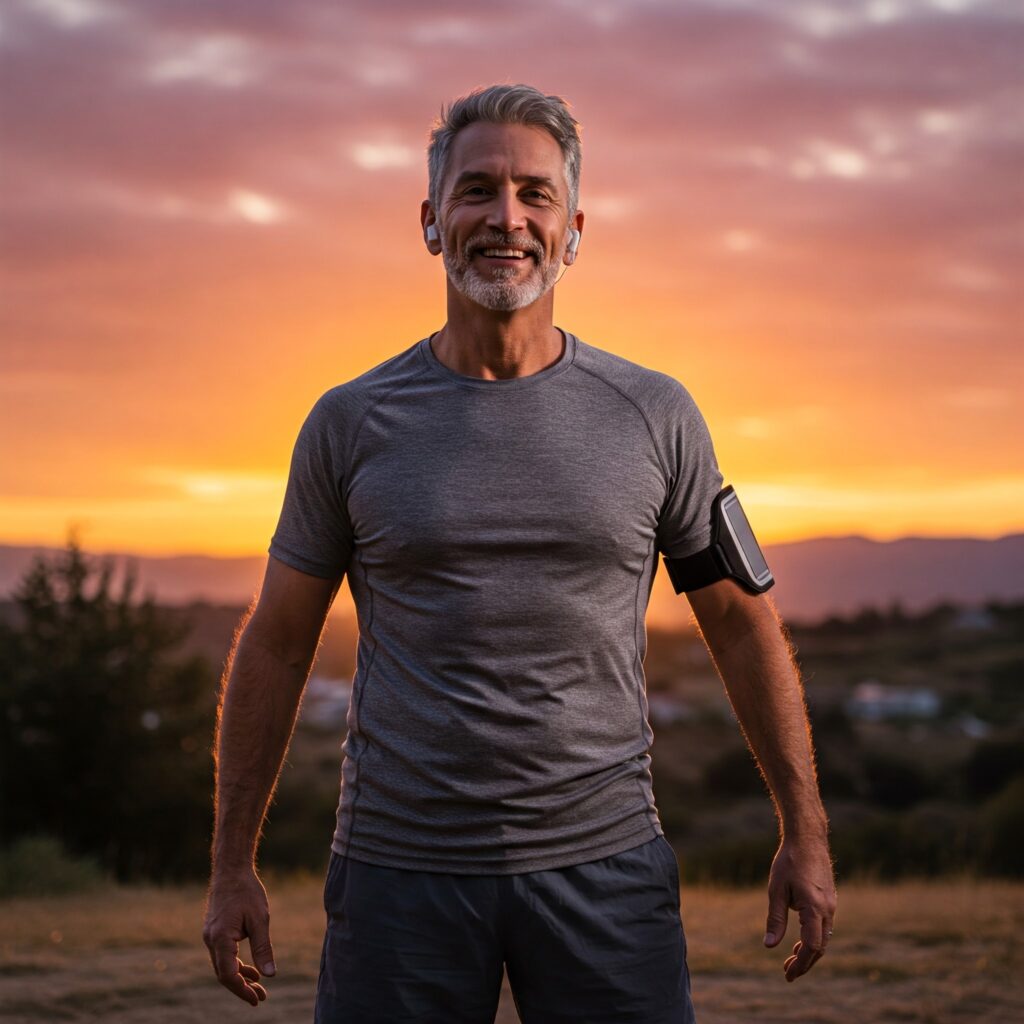

The good news is that you have significant power to influence your body’s inflammatory state through lifestyle modifications. Here are 12 actionable strategies you can implement today:
- Embrace an Anti-Inflammatory Diet: This isn’t about restrictive dieting; it’s about nourishing your body with foods that fight inflammation. Focus on a colourful array of fruits (berries, cherries, oranges), vegetables (leafy greens, broccoli, peppers), whole grains (oats, quinoa, brown rice), lean proteins (fish rich in omega-3s like salmon and mackerel, chicken, beans, lentils), and healthy fats (olive oil, avocados, nuts, seeds). Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, red and processed meats, and excessive alcohol, as these can promote inflammation. I find incorporating turmeric and ginger into my cooking adds a lovely flavour and packs an anti-inflammatory punch!
- Prioritise Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These essential fats, found abundantly in fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts, have potent anti-inflammatory properties. They can help reduce the production of inflammatory molecules in the body. Aim for at least two servings of fatty fish per week, or consider a high-quality omega-3 supplement after consulting with your GP or a registered dietitian.
- Move Your Body Regularly: Exercise is a powerful tool for reducing inflammation. Regular physical activity, whether it’s brisk walking, swimming, cycling, or strength training, can help lower levels of inflammatory markers in the blood. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, plus muscle-strengthening activities at least two days a week, as recommended by UK health guidelines.Find an activity you enjoy – that’s key to consistency!
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess body fat, particularly visceral fat (the fat around your organs), is a major driver of chronic inflammation. Losing even a modest amount of weight can significantly reduce inflammatory markers and improve overall health. Focus on sustainable lifestyle changes involving diet and exercise rather than crash diets.
- Prioritise Quality Sleep: Poor sleep can disrupt hormone balance and increase inflammation. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Establish a regular sleep schedule, create a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. I’ve noticed a huge difference in my energy levels and overall well-being since I made sleep a priority.
- Manage Stress Effectively: Chronic stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone that can have both anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory effects depending on its duration and levels. Prolonged stress can contribute to chronic inflammation. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature. Find what works for you and make it a regular part of your routine.
- Stay Hydrated: Water is essential for all bodily functions, including regulating inflammation. Dehydration can put stress on the body and potentially increase inflammatory markers. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day. Keep a water bottle handy as a visual reminder.
- Nurture Your Gut Health: The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in regulating inflammation. A diverse and healthy gut microbiome can help reduce systemic inflammation. Consume prebiotic-rich foods (like garlic, onions, asparagus, oats) that feed beneficial gut bacteria, and consider incorporating probiotic-rich foods (like yogurt with live and active cultures, kefir, sauerkraut) or a probiotic supplement after consulting a healthcare professional.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can damage the gut lining and increase inflammation in the body. Adhere to the UK’s guidelines for moderate alcohol consumption, which recommend no more than 14 units per week spread across several days.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major pro-inflammatory factor, damaging nearly every organ in the body and significantly increasing the risk of various diseases, including cancer. If you smoke, quitting is one of the most powerful things you can do for your health. Seek support from your GP or local stop-smoking services in the UK.
- Consider Anti-Inflammatory Spices and Herbs: Certain spices and herbs, such as turmeric (containing curcumin), ginger, and rosemary, have potent anti-inflammatory properties. Incorporate them into your cooking and diet. You can even try making turmeric lattes or ginger tea!
- Regular Health Checks: While not directly reducing inflammation, regular check-ups with your GP can help identify and manage underlying inflammatory conditions early on. Early detection and management can prevent chronic inflammation from progressing and potentially reduce the risk of associated diseases.
Enhancing the Benefits of Reduced Inflammation: Lifestyle Integration
Reducing inflammation isn’t just about ticking boxes; it’s about creating sustainable lifestyle changes that become integral to your daily routine. Here are some tips to enhance the benefits of your efforts:
- Be Consistent: Small, consistent changes over time yield the most significant results. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t see immediate effects. Stick with your healthy habits, and your body will thank you in the long run.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how different foods and activities make you feel. This can help you personalise your approach and identify triggers for inflammation.
- Combine Strategies: The synergistic effect of multiple anti-inflammatory strategies is often greater than the sum of their individual effects. Aim to incorporate several of the 12 tips into your lifestyle.
- Make it Enjoyable: Choose activities you genuinely like and find healthy recipes that excite your taste buds. This will make it easier to stick with your new habits long-term.
- Seek Support: Talk to friends, family, or healthcare professionals for support and encouragement on your health journey. Joining a local walking group or a healthy cooking class can also provide motivation and connection.
- Track Your Progress: Keeping a food journal, exercise log, or noting changes in how you feel can help you stay motivated and identify what’s working best for you.
- Be Patient and Kind to Yourself: There will be days when you slip up. Don’t let it derail your progress. Simply get back on track with your healthy habits as soon as you can. Remember, it’s a journey, not a race.
By understanding the profound link between inflammation, disease, and cancer, and by actively implementing these 12 strategies, you can take significant steps towards a healthier, more resilient you. It’s about empowering yourself with knowledge and taking actionable steps to reduce inflammation and enhance your overall well-being. This isn’t just about living longer; it’s about living better, with more energy, vitality, and a greater sense of control over your health. So, let’s embrace these changes and unlock our body’s incredible potential!
Join our Retirement Club
Protect and grow your business with CheeringUpInfo
Find out more about Lifestyle Improvement Club Corporate Membership
Subscribe for free lifestyle improvement tips reviews and money saving ideas
Read more lifestyle improvement articles and view videos for free
Read more articles and view videos:
- How to reduce chronic inflammation naturally UK and prevent disease
- Link between inflammation mental health and cancer uk what can I do
- Best anti-inflammatory diet for uk adults to reduce disease risk
- UK guide to lowering inflammation through lifestyle changes and cancer prevention
- What are the early signs of chronic inflammation and how to manage it UK
Relevant hashtags:
- #UKHealthMatters
- #InflammationFighters
- #DiseasePreventionUK
- #MindBodyHealthUK
- #HealthyLifestyleTipsUK
Feeling sluggish? Joints aching? You’re not alone. Many men over 55 in the UK experience these symptoms, often linked to inflammation.
But there’s hope! Discover how to reduce inflammation naturally and improve your overall health.
Visit our lifestyle improvement club to learn about the connection between inflammation and common health issues, and get expert tips on how to fight back.
Take control of your well-being today. Visit lifestyle improvement club and start your journey to a healthier you.
How to reduce chronic inflammation naturally uk and prevent disease